
FOB delivery method is a term frequently used in international trade transactions. This term, used within the framework of international trade rules determined by Incoterms, plays an important role in export and import transactions. The FOB term involves the seller loading the goods at a specific port. According to this agreement, the seller is responsible for bringing the goods to the port and loading them, and the transportation cost and risk are on the seller. The buyer, on the other hand, assumes the transportation cost and risk from the point where the goods are loaded. The FOB term clearly defines responsibilities for both the seller and the buyer, ensuring that trade transactions are conducted more orderly and securely. For this reason, the FOB term is widely used in international trade.
What is FOB Delivery Method?
What is FOB delivery method assigns specific responsibilities to the seller and buyer and determines the point at which the responsibility for the transported goods passes. This point is usually the loading port or the seller’s warehouse. In the FOB delivery method, the goods pass from the seller to the buyer starting from a certain point.
In case of a dispute between the buyer and the seller, this point is specified, and responsibility passes to the other party from this point. This way, the buyer is responsible for the shipment and other expenses of the goods, while the seller bears the risks that may occur during transportation.
FOB Delivery method is a frequently preferred transportation method in international trade, clearly defining the responsibilities transferred from the seller to the buyer. This ensures that transactions proceed smoothly without any confusion between the parties.
What Does FOB Stand For?
The term FOB, which is frequently encountered in international trade, is an abbreviation of Free On Board. The FOB term specifies when the responsibilities pass from the seller to the buyer during the transportation process of the goods.
Important Things to Know About FOB Delivery Method
- Each delivery method is paired with a specific region name. For example, FOB İzmir, EXW Denizli, CFR Hamburg, etc.
- In reality, the delivery methods in maritime transportation were previously 13. However, as a result of a regulation implemented in 2010, the number of delivery methods was reduced to 11.
- After FOB, the most commonly used delivery method in export is CIF.
- When pricing, you should know all transportation options and cost calculation methods, whether for your company or individually.
- Both parties need to be fully aware of their rights and responsibilities to resolve issues quickly.
Responsibilities of Seller and Buyer in FOB Delivery Method
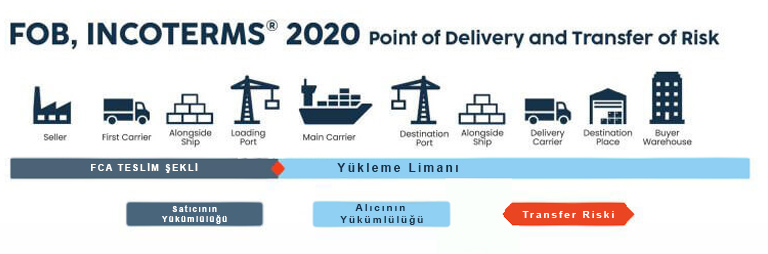
Seller
The seller loads the goods at their facilities, arranges the transportation of international cargo, performs loading at the desired place and time, and completes customs procedures.
Buyer
When the goods are loaded onto the ship, the buyer assumes all costs and risks such as overseas transportation, insurance, and customs clearance.
FAS loading method can only be applied within the scope of sea and inland waterway transportation.
The exporter’s responsibility is to provide the importer with the necessary information for customs, transportation, and insurance documents.
Distribution of Authority and Responsibilities in FOB Delivery Method
| FOB | COSTS | RISKS |
| Packaging | Seller’s responsibility | Seller’s responsibility |
| Pre-shipment (Domestic transportation) | Seller’s responsibility | Seller’s responsibility |
| Export customs | Seller’s responsibility | Seller’s responsibility |
| Loading onto main carrier (Handling) | Seller’s responsibility | Seller’s responsibility |
| Main transportation | Buyer’s responsibility | Buyer’s responsibility |
| Transportation insurance | Buyer’s responsibility | Buyer’s responsibility |
| Unloading from main carrier (Handling) | Buyer’s responsibility | Buyer’s responsibility |
| Import customs | Buyer’s responsibility | Buyer’s responsibility |
| Final transportation (Domestic transportation) | Buyer’s responsibility | Buyer’s responsibility |
What is FOB Pricing?
The seller covers the costs they incur, including shipping expenses and port fees. The seller is responsible for costs such as placing the goods on the ship, insurance, and unloading.
The buyer needs to handle transportation from the port of arrival to the final destination, along with other related costs. FOB pricing ensures a clear division of responsibilities between the seller and the buyer. In this system, the seller does not handle the process after the goods are delivered to the ship. This increases the buyer’s control and responsibility. Both parties’ rights and responsibilities are clearly defined, making it easier to resolve any disputes.




