
FCA is a delivery method listed among the Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) rules determined by the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC). FCA stands for “Free Carrier” and can be translated into Turkish as “delivery to carrier.” FCA delivery method involves the seller delivering the goods to the carrier. In this delivery method, the seller is responsible for loading the goods onto the carrier. That is, the seller is obliged to bring the goods to the vehicle transporting them and deliver them to the carrier.
The details of the FCA delivery method are determined between the seller and the buyer. Explanations regarding the place of delivery and loading are specified according to the contract made between the seller and the buyer. The location specified in the delivery method can be a point under the control of the seller. This point could be a factory, warehouse, or transportation center. It imposes certain responsibilities on the seller. After delivering the goods to the carrier, the seller is responsible for taking necessary precautions to prevent damage to the goods and for warning the carrier. However, the seller’s responsibility in FCA delivery ends once the goods are delivered to the carrier. The transportation and insurance of the goods are the responsibility of the buyer.
This is a delivery method frequently used in international trade. In this way, the delivery conditions between the seller and the buyer are clearly defined, and the rights of both parties are protected. However, it is important for the parties to specify the details related to delivery in advance and to make the agreement in writing. There are 11 different delivery methods. Delivery methods are divided into two groups: those including rules for maritime and inland waterway transportation, and those covering all modes of transportation.
Instructions covering all modes of transportation are listed below.
- EYW (Ex Works): Delivery at the Seller’s Premises
- CPT (Carriage Paid To): Delivery Paid to Carrier
- DAP (Delivered At Place): Delivery at the Named Place
- DDP (Delivered Duty Paid): Delivery with Customs Duty Paid
- CIP (Carriage and Insurance Paid To): Delivery with Carriage and Insurance Paid
- FCA (Free Carrier): Delivery to Carrier
The rules applicable to maritime transport are as follows.
- CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight): Delivery with Insurance and Freight Paid
- FAS (Free Alongside Ship): Delivery alongside the Ship
- FOB (Free On Board): Delivery on Board the Ship
What is the FCA Delivery Method?
 The rise in the world population, globalization, and technological developments have led to an even more advanced and increasingly important volume of international trade compared to previous years. This situation once again emphasizes the importance of the conditions that should already be clear in international trade, making them more explicitly defined. In search of new solutions to these ongoing problems, FCA delivery provides us with an answer. The discussions about where the goods evaluated within the scope of international trade will be delivered, who will bear the costs arising from this trade or how they will be shared between the two parties, how the insurance and transportation agreements for the products involved in the commercial activity will be made, and similar issues must be finalized with the buyer and seller involved in the trade.
The rise in the world population, globalization, and technological developments have led to an even more advanced and increasingly important volume of international trade compared to previous years. This situation once again emphasizes the importance of the conditions that should already be clear in international trade, making them more explicitly defined. In search of new solutions to these ongoing problems, FCA delivery provides us with an answer. The discussions about where the goods evaluated within the scope of international trade will be delivered, who will bear the costs arising from this trade or how they will be shared between the two parties, how the insurance and transportation agreements for the products involved in the commercial activity will be made, and similar issues must be finalized with the buyer and seller involved in the trade.
To define all these frameworks clearly without causing any potential problems, the ICC (International Chamber of Commerce) considers the list of rules called INCOTERMS (International Commercial Terms), which outline the responsibilities of the buyer and seller in commercial transactions on an international platform. The INCOTERMS, first made public by the ICC in 1936, was last updated on January 1, 2020. INCOTERMS guides us by showing the rules to follow in international trade and helps us when we face paradoxes. However, ultimately, it is not an international law, and compliance with the rules is not a legal obligation nor binding. Of course, in all commercial transactions, it is also quite possible for the trading parties to determine the commercial rules among themselves without relying on the ICC. But the main goal of the ICC is to provide a solid basis that can be referenced in banking transactions or mutual agreements that are important in international trade. This also helps to soften potential disputes that may arise.
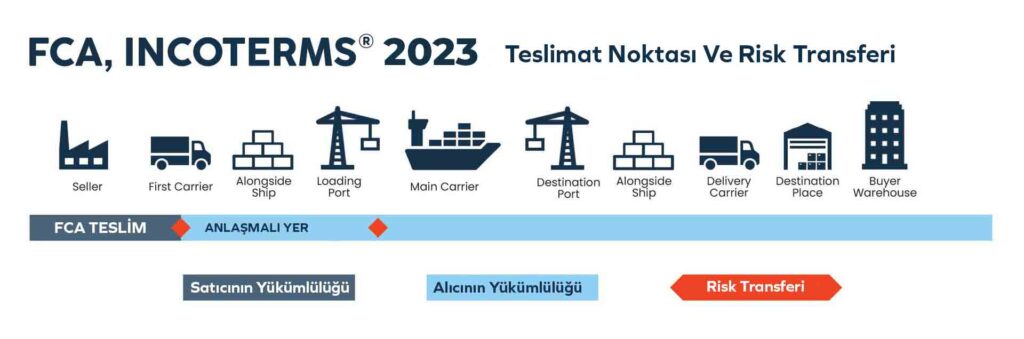
The part of the INCOTERMS rules that concerns us is the abbreviation FCA, which stands for Free Carrier. In the FCA delivery method, the exporter (seller) simply completes all customs procedures for the products, hands them over to the first carrier at a predetermined date and point, thus fulfilling their obligation. Once the goods are delivered, all responsibilities and risks related to the goods are transferred to the buyer. From this moment on, all expenses related to the goods, including insurance, agency, and freight costs, are borne by the buyer.
Advantages of the FCA Delivery Method
 The FCA delivery method offers significant advantages, especially for the seller. The FCA Incoterms rule ensures that the entire shipping process is under the responsibility of the buyer. This provides sellers with greater control and reduces risks. The transportation and insurance of the goods delivered to the buyer are the buyer’s responsibility. Companies generally prefer the FCA delivery method because it allows sellers to avoid transportation and insurance costs. Additionally, buyers have the freedom to make economical freight agreements. They can choose suitable and cost-effective logistics services according to their own shipping networks and transportation agreements. This reduces costs and makes businesses more competitive.
The FCA delivery method offers significant advantages, especially for the seller. The FCA Incoterms rule ensures that the entire shipping process is under the responsibility of the buyer. This provides sellers with greater control and reduces risks. The transportation and insurance of the goods delivered to the buyer are the buyer’s responsibility. Companies generally prefer the FCA delivery method because it allows sellers to avoid transportation and insurance costs. Additionally, buyers have the freedom to make economical freight agreements. They can choose suitable and cost-effective logistics services according to their own shipping networks and transportation agreements. This reduces costs and makes businesses more competitive.
Features of the FCA Delivery Method
In the features of the FCA delivery method, the seller completes the loading procedures by finishing customs procedures and delivers the goods at the specified location and time under the carrier’s supervision. From this moment on, all expenses and risks related to the load transfer to the buyer. Freight costs, like all other expenses, are paid by the buyer. In the FCA delivery method, the seller prepares the goods in accordance with the agreement, prepares the necessary documents required in the buyer’s country, and pays the customs fees.
If requested by the buyer, the seller arranges with the transportation agency, with all expenses borne by the buyer. The goods are delivered to the carrier or at the location and point designated under the responsibility of the transportation agency. Until the moment of delivery, all expenses and risks are the seller’s responsibility.
The goods are paid for according to the terms of the agreement. The seller is responsible for obtaining import documents or permits and paying customs duties and expenses. The most prominent feature of the FCA delivery method is these characteristics. Both parties have equal obligations and responsibilities. They pay the freight costs by agreement with the transportation agency. They receive their goods at the specified date and location. From this moment on, all expenses and risks are borne by the buyer. If the buyer instructs the seller to deliver the load to a specific person, for example, themselves or a logistics service provider who is not the carrier, the seller is considered to have fulfilled their delivery obligation once the load is handed over to this person.
Buyer's Responsibilities in FCA Delivery
The responsibilities of the buyer in FCA delivery are determined according to the FCA Incoterms rules. One of the primary duties of the buyer is to pay the purchase price of the goods as specified in the purchase agreement. This is valid just like in other delivery methods. In FCA delivery, after the seller delivers the goods, all risks are transferred to the seller.
The buyer may request documents such as loading documents, weight certificate, bill of lading, FCR customs declaration, and invoice to prove that the goods were delivered without damage. These documents serve to demonstrate that the goods were delivered in accordance with the order. To answer the question “What is FCA?”, it is a delivery method where the seller makes the goods available to




